•
Renal
problems
•
Renal
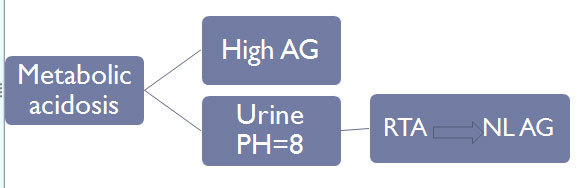
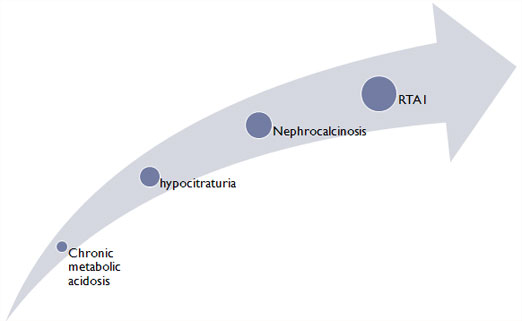
tubular acidosis
(treated
with polycitra)
•
Renal
stones
•
Bilateral
medullary calcifications(on
sonography)
•
Normal IVP
•
Cerebral
problems
•
Visual
loss(recognised
from 6 month old by mother)
•
NDD
•
microcephaly
•
Seizure(one
month)
•
Bilateral
optic atrophy
•
Delay in
P2 wave in VEP
•
Normal EEG
•
Porencephaly&agenesia of corpus collusum
•
Decresed
muscle force+increae DTR
(in
contralatelal to brain lesion)
•
Seizures&MR
•
Renal(Glomerulosclerosis
associated with chronic tubular injury &fanconi&proteinuria)
•
Ophthalmologic
(Cataracts are a hallmark of Lowe syndrome and are always present at birth).
Glaucoma, Keloids, strabismus, impaired vision
•
Growth:have
normal birth weights and lengths. By age 1-3 years, growth parameters fall below
the third percentile.
•
GI
problems(Constipation)
•
mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes
•
ventricular dilatation, cortical atrophy, and basal ganglia calcification.
•
Cardiac
abnormalities
•
Failure to
thrive
•
visual
complaints(may experience blindness because of optic atrophy )
•
hearing
loss
•
Diabetes
•
GI
manifestations
•
Psychiatric disorders
•
hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
•
nephrotic
syndrome
•
Agenesis
of corpus callosum
•
Cyctic
lesion brain(brain
stem&basal ganglia)
•
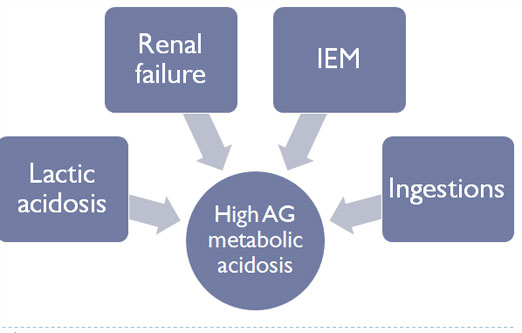
Lactic
acidosis
•
Psychomotor retardation
•
Seizure
•
Prenatal
or postnatal microcephaly may be found
•
Loss of
cortical material can result in a positive Babinski reflex, absent deep tendon
reflexes, tremors, or spastic diplegia or quadriplegia.
•
Ophthalmological examination may reveal poor visual tracking, grossly
dysconjugate eye movements, poor pupillary responses, and blindness
•
Dysmorphology(occationaly)
•
High blood
lactate and pyruvate levels with or without lactic acidemia
دکتر بابک الیاسی
رزیدنت کودکان بیمارستان لقمان
}
NDD
}
Strokelike episode & Seizure
}
Nephrocalcinosis
}
Bilateral optic atrophy
}
Metabolic acidosis
}
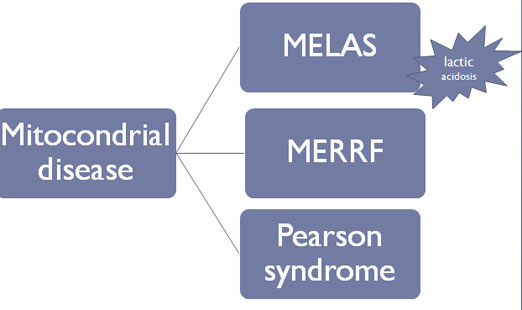
MELAS
}
mitochondrial encephalopathy with lactic acidosis and stroke-like
episodes
}
may be normal for the 1st several years
}
recurrent strokelike episodes
}
lactic acidosis
}
focal or generalized seizures,
}
hearing loss
}
Lactate/pirvate
}
Liver involvement
}
Heart involvement
}
METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA
}
lethargy, seizures, muscular hypotonia, and hypoglycemia during an
episode of metabolic decompensation
}
Microcephaly
}
pigmentary retinopathy,
}
megaloblastic anemia
}
thrombosis
}
failure to thrive,
}
developmental delay,
}
skin lesions (eg, moniliasis),
}
occasional hepatomegaly
}
facial dysmorphism
}
GLUTARIC ACIDURIA TYPE 2
}
In
contrast to the other organic acidurias, GA2 rarely presents in the
newborn period.
}
episode of metabolic decompensation with ketoacidosis, hyperammonemia,
and hypoglycemia, and encephalopathy during the first year or later,
}
Macrocephaly
}
seizures,
}
Metabolic stroke(porencephaly,volume loss)
}
Corpus collusom agenesis
}
Optic atrophy
}
1-Neurodegenerative Disorders :
}
Juvenile GM2gangliosidosis
}
KRABBE DISEASE
}
METACHROMATIC LEUKODYSTROPHY
}
2-Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathies
}
MELAS
}
MYOCLONUS EPILEPSY AND RAGGED RED FIBERS:
}
myoclonic epilepsy
}
mitochondrial myopathy
}
optic atrophy
}
peripheral neuropathy
}
Spasticity
}
LEBER HEREDITARY OPTIC NEUROPATHY
}
LEIGH DISEASE
}
LEIGH DISEASE
}
Most cases become apparent during infancy with feeding and swallowing
problems, vomiting, and failure to thrive. Delayed motor and language
milestones may be evident, and generalized seizures, weakness,
}
hypotonia, ataxia, tremor, pyramidal signs, and nystagmus are prominent
findings. Intermittent respirations with associated sighing or sobbing
are characteristic and suggest brainstem dysfunction. Some patients have
external ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, optic atrophy, and decreased visual
acuity.
}
Elevations in serum lactate levels are characteristic



